Recently, the lily breeding team of the Institute of Vegetables and Flowers of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) has published a research paper titled “LlLRP1, an SHI/SRS Transcription Factor, Mediates Bulbil Formation in Lilium lancifolium via Regulation by LlWOX11 and Response to NaCl Stress” in the International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (IF = 8.5).

Lilium lancifolium, a traditional Chinese lily used for both food and medicinal purposes, has a wide distribution and extremely high economic value. In recent years, it has been widely cultivated in many regions as a characteristic agricultural product. Bulbil propagation, as its main natural propagation strategy, boasts the advantage of preserving the excellent traits of the female parent and holds broad application prospects in production. However, the molecular mechanism regulating bulbil formation remains unclear.
In this study, L. lancifolium was used as materials and transcriptome analysis and molecular biology experiments were conducted to identify the SHI/SRS transcription factor LlLRP1 for the first time. This factor is transcriptionally activated by LlWOX11, and regulated the formation of axillary bulbils. Under salt stress, the expression level of LlLRP1 increases rapidly and promotes the expression of antioxidant enzyme genes (SOD, ROS), indicating that it has dual functions in bulbil development and stress adaptation. This finding not only enriches the regulatory mechanism of bulbil formation in L. lancifolium but also provides a theoretical basis for realizing artificial regulation of plant bulbil formation.
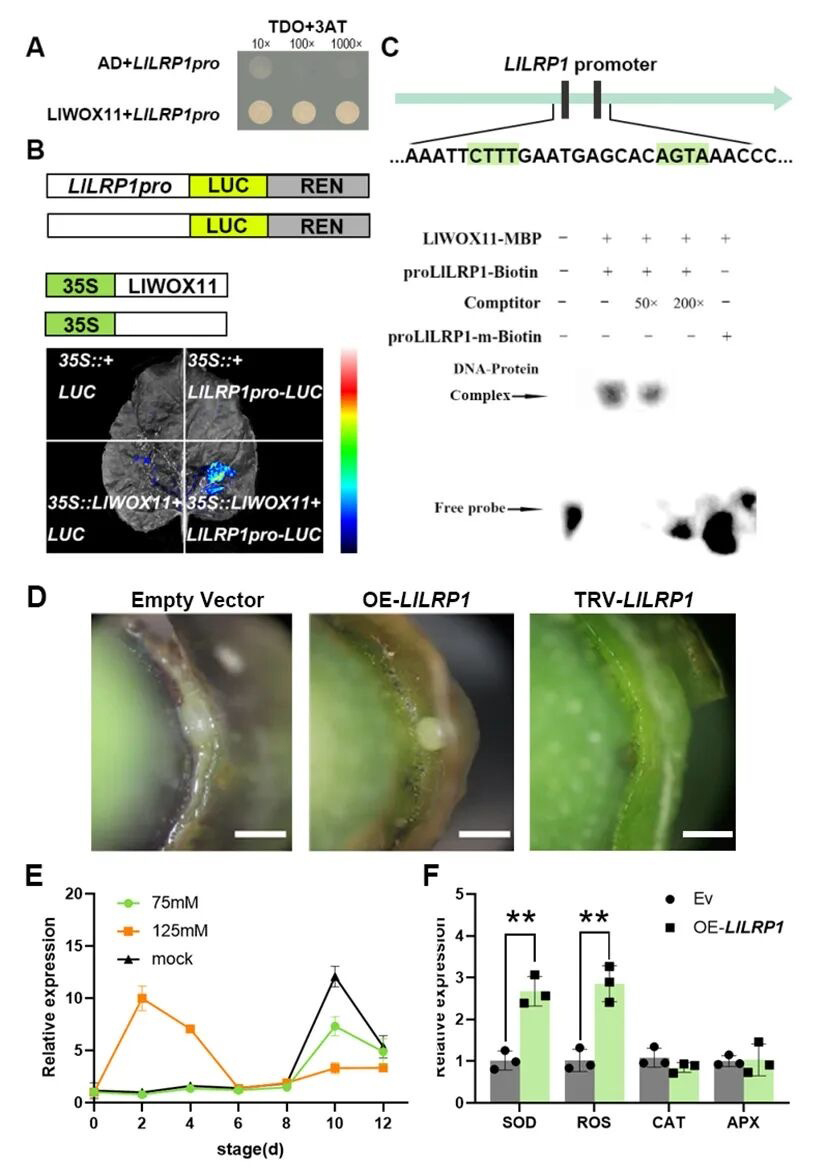
LlWOX11 binds to the promoter of LlLRP1 to promote bulbil formation in L. lancifolium and respond to salt stress.
The Institute of Vegetables and Flowers, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, is the lead institution for this work. Ph.D. candidate Bai Jingyi and Assistant Researcher Yang Panpan are the co-first authors, while Researcher Ming Jun and Assistant Researcher Yang Panpan are the co-corresponding authors. This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFD1001002) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32172612, 31902043).
Link:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.147385