Recently, the Quality and Safety Team of the Institute of Vegetables and flowers, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, has developed a precise and sensitive immunoassay based on DNA tetrahedron spatial mediation, enabling the precise and sensitive detection of imidacloprid residues. This provides a new approach for monitoring the small-molecule chemical pesticides residue in agricultural products. The related research results are titled “Study of the sensitization mechanism of an immunoassay based on DNA tetrahedron spatial mediation for detecting imidacloprid in vegetables” was published in the Journal of Advanced Research (IF= 13.0, Q1).

Neonicotinoid pesticides are currently one of the most widely used insecticides, but their misuse poses a threat to human health. Therefore, a precise and sensitive immunoassay can help assess the pesticide residue status of a large of fresh vegetables in China in a short period of time and improve the vegetable quality and safety early warning system. However, the established immunoassays existed drawbacks such as physical adsorption of labeled antibodies leading to disordered spatial overlap of antibodies, and spatial steric effects by vegetable matrices causing masking of antibody recognition sites, resulting in immunoassay sensitivity that fails to meet detection requirements.
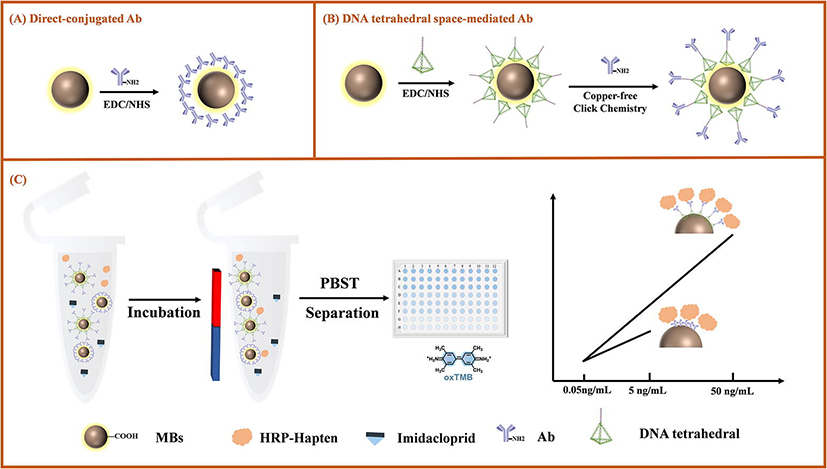
Figure 1. (A) Traditional immunoprobe (B) DNA tetrahedron space-mediated immunoprobe (C) Schematic diagram of immunoassay
To address the above issues, this study intends to employ the precise addressability tetrahedron DNA frame nucleic acid to spatially mediate the orientation of antibodies, utilizing arm chain covalent coupling technology to directionally mediate labeled antibodies, thereby establishing a precise and sensitive immunoassay based on DNA tetrahedron spatial mediation for neonicotinoid pesticides. By utilizing DNA tetrahedron to spatially mediate antibodies, it is possible to achieve targeted antibody and control the complete exposure of antibody recognition sites. The DNA tetrahedron space-mediated immunoassay was successfully applied to detect imidacloprid pesticide residues in vegetable samples such as Chinese cabbage, cucumber, and zucchini. Compared with traditional immunoassay, the DNA tetrahedron space-mediated immunoassay demonstrates significantly improved sensitivity and a linear range expanded by one order of magnitude.
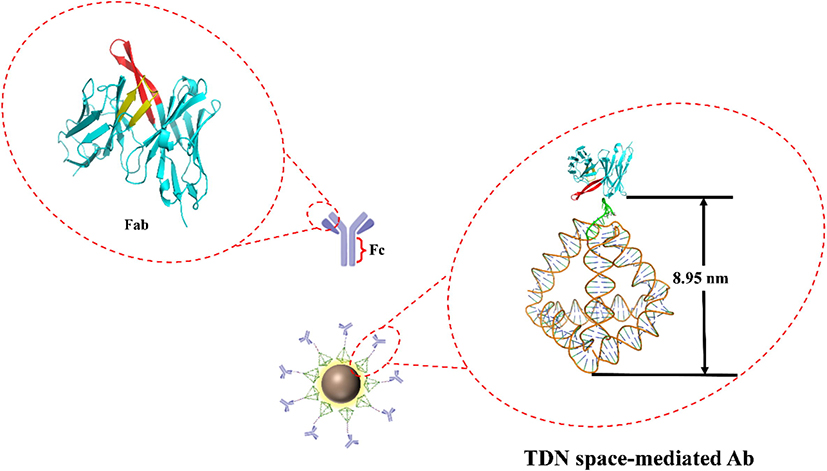
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of DNA tetrahedron space-mediated antibodies.
This study addresses the urgent need for timely regulation of vegetable quality and safety in China, aiming to overcome low sensitivity limitations of immunoassay. The study seeks to enhance the monitoring efficiency for pesticide residues in vegetables, providing a theoretical foundation for quickly assessing the pesticide residue status of a large volume of fresh vegetables in China and ensuring the safe supply of vegetables to the public.
The Vegetable and Flower Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences is is the lead institution for this work. Assistant Researcher Chen Ge and Researcher Xu Donghui are the co-corresponding authors, and Dr. Zhai Rongqi is the first author. The study was conducted at the National Key Laboratory of Vegetable Biotechnology Breeding and the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs Key Laboratory of Vegetable Quality and Safety Control, and was supported by the Special Fund for the Industrial System Construction of Modern Agriculture of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Web site of the paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2025.06.082